
Agridisk
Egypt - Alexandria

Food Tech | What is the new technology in the food industry 2024?
Description: In the current age of advanced technologies, the dawn of food technology has introduced innovative and efficient techniques in the food industry. This rapidly developing sector combines science, agriculture, and technology to enhance food production, storage, and delivery, providing impactful solutions to pressing global issues such as food waste and security. The prevalence of food tech signifies a dramatic evolution in mankind's approach to food, crossing the boundaries of conventionality and embracing the future. This fascinating and transformative subject warrants a deeper understanding of its essence, its impact on the food industry, the groundbreaking innovations it fosters, hurdles it encounters, and its potential prospects. Food technology represents the cutting edge intersection of tech wizardry and good old fashioned human sustenance: food. To put it in elementary terms, food technology is the application of various technological achievements into the world of food production, processing, preservation, and consumption. First and foremost, it's important to clarify that food technology isn’t about turning peaches into robots. Food tech involves every stage in the journey of food production, from farm to fork. Every phase has been improved or in some cases revolutionized by technological advances, creating a more streamlined, efficient and safe supply chain. For starters, let's talk about agriculture, the birthplace of every food item. The natural process of growing crops has evolved exponentially thanks to a slew of tech innovations. Farmers now employ tools such as drones, satellite imagery, and GPS technology to monitor crop conditions, maximize yield, and minimize expenses. One could argue that even the humble tractor, when tricked out with the latest GPS tech, represents, the heart and soul of food tech for the farming industry. From the sprawling fields, the food moves towards processing units where it is cleaned, sorted, packaged, and sent on its way. This is where machinery and automation come in. These powerful tech beasts sort through tons of produce in minutes, identify imperfections, and provide packaging solutions that are safe and hygienic yet sustainable. Then there are breakthroughs in preserving food freshness. From controlled-atmosphere storage to individual quick freezing, technology has made the unimaginable conceivable: Enjoying fresh strawberries in the dead of winter or savoring Mexican guacamole in Tokyo! When food technology arrives at the table, on demand food delivery apps such as Uber Eats or Grubhub, automated food making machines like pizza and pancake bots, or smart cooking devices like Instant Pots and smart coffee makers all come to mind. Arguably more important than merely making life delicious, food technology also has a pivotal role to play in addressing some humanity’s biggest challenges like hunger, malnutrition, waste, and sustainability. From biofortified crops that offer enhanced nutritional value to biodegradable food packaging that reduces waste, food technology’s potential to tackle these grand global problems cannot be underestimated. In conclusion, this is food technology: ever changing and boundlessly innovative. It’s not just about creating neater ways to deliver a pizza, nor is it confined to discussions about the next kitchen gadget. It’s a field that’s at the core of human survival, health, and happiness, and that’s why it deserves nothing less than your full attention! With its capacity for efficiency, improvement, and ingenious solutions, food technology forms a vital cog in the complex machine of our food ecosystem. This is more than mere tech hype. It’s the future of food, today. Continuing the fascinating exploration of food tech, it's crucial we delve further into the revolutionary trends that are shaping the food industry, apart from what has already been discussed. One standout element is the application of blockchain technology in the food sector. It's no longer merely about cryptocurrencies - blockchain is now transforming the food industry by ensuring transparency and traceability. Not only does it allow consumers to see each step of the product's journey - from farm to table – it also provides a reliable way to prevent food fraud. Closely tied with blockchain is the evolution of Internet of Things (IoT) in the food industry. IoT-connected devices are increasingly used to monitor food storage conditions, ensuring products are kept at optimal temperatures during transport and storage to maintain their quality and safety. Coupled with the power of Big Data, these IoT-driven insights can predict consumer trends, reduce waste and optimize supply chain efficiencies. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is another powerhouse revolutionizing food tech. AI is enabling smarter and quicker decision-making in agriculture. By utilizing machine learning algorithms to analyze data from soil sensors and weather reports, farmers can adopt precise farming strategies. Besides, AI is making a crucial contribution to food quality control, identifying defects, and contamination faster and more accurately than the human eye. 3D food printing is yet another fascinating bit of innovation. Though in its infancy, it holds tremendous potential - transforming the way food is produced, presented and consumed. It can allow consumers to customize nutritional content, appearance, and flavor of their food, making cooking a truly personalized experience. Lab-grown meat, a mind-boggling outcome of advanced biotechnology, is also worth the discussion. This futuristic idea of cultivating meat from animal cells in a lab might not only offer a sustainable solution to meet global meat demand but also have significant implications for animal welfare. Perhaps the sleekest innovation is the rise of robotic restaurants. In this tech-driven model, robots carry out the preparation and serving of meals, speeding up service, and minimizing human errors. In a nutshell, from blockchain to robotics, AI to 3D printing, the future of food is being dramatically rewritten by technology. As we progress into this innovative era, it becomes clear, embracing these more sustainable, efficient, and ethical practices in food tech is not just a choice - it's an absolute necessity. So, as you take your next bite, spare a thought for the hidden tech that made it possible. It's a brave - and delicious - new world out there! As the world continues to embrace technological advancements in various sectors, food technology hasn't been left behind. Two buzz words trending in the food industry right now are blockchain and the Internet of Things (IoT). Blockchain, originally made famous by Bitcoin, has numerous advantages to the food industry. The capability to offer transparent and secure transactions, for instance, is transforming supply chains. Consumers are growing more conscious of their food’s origin and producers are under pressure to deliver this transparency. How? By recording each stage of the food's journey, from the farm to the table on a public ledger. Blockchain also allows for swift traceability in the event of a food safety issue, allowing companies to pinpoint and address problems more rapidly than traditional methods. On the other hand, IoT is automating and digitalizing the manufacturing process. IoT devices help monitor environmental conditions that favor optimal food production and storage. They also play a major role in transport logistics, ensuring perishable goods maintain the required temperature during transit. It’s now ordinary to witness manufacturers remotely monitor and manage their production lines employing IoT devices. Artificial Intelligence (AI), not to be overshadowed, is revolutionizing agriculture and food quality control. The use of AI-powered drones, robots, and algorithms is taking smarter farming to a new level, aiding farmers to identify various plant diseases, predict climate change, and make strategic decisions. AI is also enhancing food freshness as robots now have the capability to analyze food quality factors such as color, freshness, appearance, and odor. A wave of innovation that may seem like a page from a sci-fi novel is 3D food printing. However, it’s now a fact. This technology opens up opportunities for preparing food with the perfect proportion of nutrients without any waste. Not only is it allowing customization at a new level but it's also facilitating the creation of intricate shapes and patterns, throwing the culinary world into a creative frenzy. Talking about creativity, the concept of lab-grown meat or 'cultured meat' is setting a new frontier in food technology. This innovation could potentially mitigate the environmental costs of livestock farming, address animal cruelty concerns, and cater for the increasing global demand for protein. Last but not least, robotic restaurants are gradually becoming part of the new normal. Due to hygiene concerns and demand for quicker service, robots are being employed as cooks and waitstaff. They not only work tirelessly and free from human error, but also offer an unforgettable futuristic dining experience. Undoubtedly these technological transformations in the food sector are prominent indicators of a more precise, sustainable, and efficient future. The food and technology marriage gives everyone at the table something to savor while solving some of the pressing challenges in the food industry. As much as we celebrate the advancement in food tech, it's important to note this burgeoning field also faces its share of challenges. From logistical concerns to potential socio-economic consequences, we can't ignore the difficulties that come with the shift to hi-tech solutions in the food industry. This raises the critical question: What are the major challenges faced by the food tech industry? First and foremost, the implementation of these advanced technologies calls for significant capital investment. Be it the use of AI or IoT in food manufacturing, a revamp of existing infrastructure is essential. This means businesses, particularly smaller ones, often grapple with the financial burden of keeping up with the pace of innovation. In the realm of blockchain and smart contracts, while it ensures traceability and reduces fraud, its implementation poses a technical challenge. The lack of knowledge and expertise around blockchain technology can hamper its acceptance within the food industry. It's a similar issue with 3D food printers – these devices require skilled professionals to operate and maintain them, setting up a steep learning curve. Lab-grown meat, though a promising field, confronts both public perception and regulatory challenges. As it's a new concept for consumers, there's skepticism around taste and quality that these brands need to overcome. From a regulatory standpoint, the approval process is often lengthy and complex, slowing down market access. IoT’s role in food storage and manufacturing is yet another concern. While it poses excellent opportunities for customizing food storage conditions, there's the threat of cyber-attacks. This challenges food tech companies to ensure absolute protection against data breach and leakage – a task easier said than done. Artificial Intelligence, particularly in food quality control and agriculture, has stirred a debate around job displacement. The automation of these processes means potential job losses, aggravating social inequality. Robotic restaurants, known for impeccable precision and efficiency, grapple with a lack of human touch. As the hospitality industry thrives on personal interaction and customer service, the emotional connection that humans offer can't yet be replaced by robots. Further, the issue of sustainability looms large over the industry. Biodegradable packaging, though a step in the right direction, still has a long way to go before it can completely replace plastic and other environmentally detrimental materials. Yes, food tech is changing our world, but it must also learn to navigate the complex challenges it faces. Some are growing pains, others are deeply entrenched socio-economic issues that society must confront. Ultimately, success in food tech will not just be about innovation and efficiency, but also about sustainability, inclusivity, and adaptability. As tech enthusiasts, let's not just adopt and applaud technological advancement, but also critically examine the hurdles it must conquer to truly revolutionize the food industry. Looking ahead, the food tech industry hints at possibilities that seem to have been drawn directly from a high-tech science fiction narrative. Blockchain and Internet of Things (IoT) will continue to innovate. What's more, do not be surprised if a robot hands you the next plate in the restaurant. Blockchain technology promises to bring transparency and security to the food sector by tracing food items from the farm to the table accurately. This technology's adoption could thereby address issues related to food safety and traceability. Moreover, the Internet of Things (IoT) has a vast potent application in the food industry. From real-time monitoring of crop fields to intelligent tracking of storage conditions in the supply chain, IoT can dramatically increase efficiency and accuracy in food production and distribution. Artificial Intelligence (AI) not only stands to transform agriculture through predictive analysis of weather patterns and crop diseases but also has immense potential in maintaining food quality control. Automated detection of contamination or defects, anyone? The realm of 3D food printing is truly fascinating. Who wouldn’t like a pizza perfectly customized to their taste and nutritional requirements, topped with a little creativity? As this technology matures, customizable and creative food preparation could become a mainstream reality. Lab-grown meat is another rising star in the food tech sphere. Not just chicken nuggets, but actual cuts of meat grown from cells in a lab. The technology could address concerns related to the environmental impact and animal welfare issues prevalent in traditional meat production. Lastly, while the idea of robotic restaurants may appear too futuristic to some, they are already a reality in some parts of the world. Allowing for consistency and increased hygiene, robots might soon be serving your food, automating the food industry like never before. However, these fascinating developments in food technology are not without their barriers and challenges. Capital investments needed to adopt cutting-edge tech, technical issues, a lack of knowledge implementing blockchain, and smart contracts present significant hurdles. The lab-grown meat industry faces a major obstacle in overcoming consumer skepticism and obtaining regulatory approval. Furthermore, as IoT devices become widespread in the food industry, cybersecurity concerns will also need to be addressed diligently. As AI continues to automate processes, there are legit concerns about job displacement and handing over too many human roles to machines. Robotic restaurants, while efficient, lack the human touch and could impact the overall dining experience. Undoubtedly, while strides are being made towards biodegradable packaging, there's still a long way to go in ensuring a sustainable future for the food tech industry. In essence, although the future of food technology appears extremely promising, addressing these challenges, from technological to socio-economic aspects, will be crucial for the industry's real success. To wrap up, the aliment of tomorrow won’t just be farm to fork, but also tech to table. Food technology is indubitably a vital piece of our future. As we navigate into an era progressively defined by technology, there will certainly be greater opportunities for innovation in the realm of food technology. Despite the challenges that may lie ahead, such as food safety concerns and regulatory complexities, it's crucial to not lose sight of the profound potential of food technology to revolutionize how we produce, distribute, and consume our food. With continuous research and development, mankind can optimistically anticipate an advanced food industry where sustainable and high-quality food is available to all, marking the culmination of the promising journey of food technology. The nexus of technology and food production heralds a pivotal shift in how we cultivate, consume, and conceive the very notion of sustenance in our modern world. As we inch closer to the mid-21st century, we stand at the cusp of a revolution that seeks to reconcile the pressing need for food security with the imperative of environmental stewardship. This essay endeavors to untangle the intricate threads of sustainable food production, diving into the transformative power of precision farming, vertical agriculture, and the bold new world of GMOs. We will traverse the landscape of alternative protein sources, shedding light on the innovative substitutes reshaping the food industry. The journey extends into the realm of food preservation and shelf-life extension, revealing cutting-edge strategies that promise to alleviate global food waste. Personalized nutrition surfaces as a beacon of hope, marrying technology with individual health, while advancements in food safety and traceability beckon a future where transparency reigns supreme in our quest to nourish an ever-growing population. The burgeoning field of food technology is a cornerstone in the transformative movement toward sustainable agricultural practices. This discipline is not merely peripheral; it is a vital nexus of innovation, efficiency, and environmental stewardship. By harnessing cutting-edge technological advancements, food science is redefining the parameters of what it means to produce food responsibly in a world of burgeoning populations and diminishing natural resources. Central to this shift is the development of precision agriculture, which utilizes data analytics, satellite imagery, and IoT devices to optimize farming practices. The pinpoint accuracy of these tools allows for the judicious application of water, fertilizers, and pesticides, which in turn mitigates soil depletion, reduces runoff into waterways, and lowers greenhouse gas emissions. Micro-level monitoring creates a macro-level impact – a testament to the potency of targeted interventions. Another facet of food technology that is effectively recalibrating sustainability metrics is the synthesis of alternative proteins. Plant-based and lab-cultured meats diminish the ecological footprint of protein production by furnishing alternatives to traditional animal husbandry. The outcomes are a substantial reduction in land use, water consumption, and greenhouse gas output. By transitioning dietary staples to systems that demand less of the planet's limited resources, these innovations are essential contributors to a more frugal and thoughtful approach to food production. The exploration and integration of vertical and urban farming stand as poignant examples of how space and resource limitations can be creatively addressed. Multi-level cultivation systems leverage vertical space, reduce the need for arable land, and enable proximity to urban centers, thereby slashing transportation emissions and related spoilage. The application of controlled environment agriculture within these systems ensures year-round growing cycles, independent of climatic uncertainties, and underscores an age where technology serves as both shield and spear in the face of global food challenges. Moreover, the development of biodegradable packaging materials derived from food waste exemplifies a circular economy ethos within food technology. Through the employment of these sustainable materials, the sector aims not only to reduce the environmental harm caused by plastic waste but also to valorize byproducts that were previously deemed economically useless. This approach illustrates a dual triumph in reducing the ecological impacts of both food production and waste management. In analyzing food waste itself, food technology is instrumental in devising systems for improved shelf life, efficient supply chain logistics, and predictive analytics to match supply with demand. Technologies that extend the longevity of perishable goods or that facilitate the redistribution of surplus items are integral to curtailing food wasting – a pivotal step toward a more sustainable agricultural paradigm. When viewed through a telescopic lens, the arc of food technology is bending unmistakably towards sustainability. The vitality of these scientific endeavors lies in their capability to cohere with the natural world while concurrently elevating the calibre and scope of agricultural productivity. It is through the deployment of these sophisticated, yet elegantly designed food technologies, that a new epoch in sustainable agriculture is not simply envisioned, but actively constructed. In summary, the gravitas of food technology in the grand schema of sustainable agriculture cannot be overstated. It is the vanguard of an agronomic revolution, marrying scientific foresight with environmental rectitude. Each technological stride serves as a tangible stride toward alimentary abundance that treads lightly upon the Earth—a beacon of progress in the ceaseless quest for agricultural congruence with our planet's ecological boundaries. Emerging Frontiers in Alternative Protein Synthesis: Enzymatic Tailoring and Microbial Fermentation The domain of alternative proteins stands at the precipice of transformative shifts, driven by sophisticated biotechnological advancements and innovative research methodologies. Acknowledging the global urgency to sustainably feed an ever-growing population, the scientific endeavor has expanded beyond plant-based and lab-cultured meats. Researchers have pivoted to novel techniques in the synthesis of alternative proteins that promise unparalleled efficiency and ecological congruity. A significant breakthrough in this expanse is the burgeoning field of enzymatic protein tailoring. With the precision of a master artisan, enzymes, nature's catalysts, are being harnessed to modify alternative proteins at the molecular level. This manipulation endows the proteins with attributes akin to their animal-based analogs, such as improved texture, flavor, and nutritive value. The enzymatic process is not only exquisite in its precision but also remarkable in its reduced energy footprint, aligning closely with the tenets of sustainable production. Parallel to these endeavors is the resurgence of microbial fermentation as a powerhouse for protein generation. Utilizing microorganisms such as fungi, algae, and mycoprotein, fermentation technologies are creating proteins that are highly scalable and nutrient-dense. The utilization of single-cell proteins, derived from microorganisms grown in controlled bioreactors, has emerged as a stellar embodiment of this technique. These microscopic agents of change are proving to be a veritable cornucopia, capable of producing vast quantities of high-quality proteins from simple substrates such as carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and renewable energy sources. The integration of these methods with genomic editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9 has imbued the field with an unprecedented capacity to craft and optimize proteins. Researchers can now edit the DNA of microorganisms to enhance their protein production capabilities, fine-tune the nutritional profile of the resulting proteins, or even design entirely new proteins that possess desired functionalities – a monumental leap in the tapestry of alternative protein research. These breakthroughs signify more than mere technological progress. They represent a harmonizing force between human ingenuity and the imperative of ecological stewardship. Through the advancements described, the production of alternative proteins can be viewed in a new light – not as a mere supplement to traditional animal proteins, but as a sophisticated, multi-dimensional strategy that elevates the potential for a balanced coexistence with our planet's finite resources. The implications for food security, environmental resilience, and human health are profound, cementing alternative protein research as a cornerstone in the agenda for an equitable and sustainable future. As we progress beyond what was once a primitive understanding of agricultural science and food technology, contemporary methodologies emerge to extend shelf life and enhance food preservation. It is within this modern framework that new technologies demonstrate their pivotal role in the fortification of our food supply against the deterioration that stems from both biological and abiotic factors. Advancements in Active and Intelligent Packaging Systems stand on the forefront of these endeavors. Active packaging refers to a system that interacts with the food to maintain its quality and extend shelf life. Innovations in this area include the development of materials that can regulate the atmosphere within packaging. Oxygen scavengers, for example, are incorporated into packages to absorb residual oxygen, thereby mitigating oxidation and rancidity of fat-rich products. Ethylene absorbers, conversely, prolong the freshness of fruits and vegetables by removing the ethylene gas they emit, which accelerates ripening and can lead to premature spoilage. Intelligent packaging technology embraces the sophistication of sensing and indicator systems that convey the internal conditions of food packaging or the quality of the food itself. Time-temperature indicators, for instance, monitor and provide a visual account of the cumulative temperature exposure of products, which is essential for items sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Another groundbreaking technology is the application of High-pressure processing (HPP). HPP uses intense pressure to inactivate spoilage microorganisms and enzymes without the need for additive chemicals, thus extending shelf life while maintaining the nutritional value and sensory characteristics of foods. Unlike thermal processes, which can degrade the quality, HPP-treated foods retain a more fresh-like state. Furthermore, the field of nanotechnology has made strides in providing novel solutions to enhance food preservation. Nanocoatings, merely a few molecules thick, can provide an impermeable barrier to gases such as oxygen, or even to moisture. These nanomaterials may also release antimicrobial substances that further protect against microorganisms that could otherwise spoil foodstuffs. In the realm of Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP), calculated alterations of the gaseous environment within packaging materials greatly curb the metabolic rates of perishable products, thus slowing down spoilage. This adaptation of the atmospheric composition - often an increased level of carbon dioxide and a reduced level of oxygen - can significantly prolong the shelf life of fresh produce, meats, and baked goods. Additionally, the exploration of Edible coatings opens possibilities for both prolonging the shelf life of food and providing an extra layer of nutrients. Derived from proteins, polysaccharides, or lipids, these coatings can act as moisture barriers, gas diffusers, or carriers for added food preservatives. Notably, when created from natural and food-grade materials, these coatings can be consumed along with the product, offering a no-waste advantage. Preservation technologies such as Advanced Cooling and Smart Refrigeration have made substantial contributions as well. Leveraging precise temperature control and atmospheric monitoring, these systems ensure that foods are held in conditions that greatly reduce the rate of spoilage. Drawing on these sophisticated techniques, society is not only witnessing an extension in food shelf life but is also engaging with a form of sustenance optimization that addresses the challenges of resource conservation and environmental respect. The symbiotic relationship between food science and technological innovation reveals a concerted effort to maintain and distribute high-quality, nutritious foods across a global scale. This mosaic of advancements portrays a clear message: that the endeavor to extend food shelf life is equally about ensuring global food security and fostering a more sustainable interaction with our planet's invaluable resources. Advancements in Nutrigenomics: The Core of Personalized Nutrition The pursuit of personalized nutrition is an emerging discipline intersecting the domains of genomics, biotechnology, and nutritional sciences, aiming at tailoring dietary recommendations to individual genetic profiles. As the understanding of the human genome has deepened, so too has the grasp of how genetic variations affect nutrient metabolism and overall health. Nutrigenomics, a cornerstone of personalized nutrition, has made significant strides. This scientific area investigates how different nutrients affect gene expression, revealing that nutrition can enact a modulatory role at the genomic level. We have now begun to catalog how single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) influence individual responses to specific dietary components, which is essential for constructing personalized eating plans. This understanding is also central to preventing diet-related diseases on a more individualized basis. Advances in computational biology and bioinformatics facilitate high-throughput dietary intake data analysis, enabling precise identification of nutrient-gene interactions. These computational tools assist in the development of algorithms that predict individualized responses to diet, thus aiding nutritionists and healthcare providers in formulating highly bespoke dietary guidelines. Metabolomics, an allied field, complements nutrigenomics by providing an analysis of metabolic profiles that reflect the biological response to dietary intake. Through this, scientists have developed biomarkers that offer insights into an individual's nutritional status, informing more accurate dietary adjustments. The combination of genotypic and phenotypic data offers an exquisitely detailed picture of one's nutritional needs. Personalized nutrition has also spurred innovation in the field of probiotics and the study of the microbiome. Research now suggests that modulating gut flora through tailored probiotic formulations may ameliorate various pathologies, from obesity to inflammatory bowel disease. The cross-talk between diet, microbiome, and health emphasizes the need for personalized probiotic interventions as part of a comprehensive nutrition strategy. Digital health technologies, such as wearables and smartphone apps, have begun to find their place in personalized nutrition, by tracking biosignals and dietary intake in real-time, and providing immediate feedback. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms analyze this wealth of data, recommending dietary modifications that could lead to optimized health outcomes for individuals. Finally, advancements in educational efforts have disseminated knowledge about personalized nutrition more widely amongst both professionals and the public, fostering a better understanding and appreciation for this cutting-edge approach to dietary science. To encapsulate, significant progress toward personalized nutrition reflects a confluence of advanced genomic research, innovative digital health solutions, and an enriched understanding of the human microbiome. Collectively, these advancements forge a more nuanced and efficacious approach to nutrition, promising enhanced health outcomes tailored to individual genetic, metabolic, and lifestyle determinants. This sphere of science continues to expand, holding potential for profound impact on public health and personalized dietary recommendations. It is within this matrix of dynamically evolving disciplines that the future of nutritional science and its applications to individual health and well-being is being vigorously shaped. Blockchain Technology Enhancing Traceability in the Food Supply Chain The emergence of blockchain technology holds the potential to revolutionize the manner in which the traceability of food products is managed within the supply chain. A decentralized ledger system, inherently secure in its architecture, facilitates the transparent logging of the journey of foodstuffs—from harvester to consumer. This technology underpins a transformative approach to quality assurance, allowing for real-time tracking that is virtually immutable and hence, trustworthy. With its capacity to store data points at each exchange—such as geographic location, temperature conditions, and timestamps—blockchain technology enables a rapid and precise investigation in the event of foodborne disease outbreaks or contamination incidents. The benefits extend beyond safety; such stringent control of the supply chain enhances trust in food producers and bolsters brand reputation. Moreover, this fine-grained level of detail offers consumers a clearer view into the provenance of their food, allowing informed purchasing decisions that could inspire shifts towards more sustainable and ethical consumption habits. Integration of Smart Sensors and Food Safety Technology has advanced to where smart sensors are employed extensively within the context of food safety. These devices are critical in monitoring conditions that could affect the quality and safety of food products. By utilizing advanced biosensors, critical parameters such as pH levels, temperature, moisture content, and the presence of contaminants can be continually assessed. This lends credence to preemptive action protocols, such as triggering alerts when a product is in danger of spoilage or has been exposed to conditions conducive to pathogenic microbial growth. These smart sensors are becoming increasingly sophisticated, offering higher specificity and sensitivity, as well as ease of integration into existing packaging and supply chain systems. What's more, the miniaturization of sensor technology aligns with the overarching trend towards less invasive monitoring. Subsequently, there is less interruption to standard operation procedures, making the adoption of these technologies more palatable to food businesses of varying scales. Advanced Traceability and its Role in Regulatory Compliance Regulatory frameworks governing food safety are continually evolving to incorporate technological capabilities. Central to these regulations is the necessity of comprehensive traceability systems that can pinpoint the origin and transit of products within the food chain. Advanced traceability systems, fuelled by technological innovations, now offer unprecedented precision in mapping food pathways. These systems not only support compliance with governmental standards but also facilitate international trade by ensuring alignment with global food safety protocols. The deployment of such systems can deliver economies of scale for businesses endeavoring to enter new markets, further fueling the impetus for maintaining a vanguard position in food safety and traceability technologies. Concluding Note The development and implementation of technology within the realms of food traceability and safety is an unfolding narrative. A confluence of dynamic technologies—blockchain, smart sensors, and advanced traceability systems—show promise in not only managing but also forging new paradigms in food quality assurance. As this technological nexus continues to evolve, so too does the capacity to ensure the integrity, safety, and sustainability of food supplies worldwide. Each stride made in these areas not only reflects an advancement in scientific understanding but also demonstrates a commitment to preserving consumer health and enhancing the veracity of the global food network. The study and refinement of these technologies, as well as their integration into existing food systems, represent a marriage of scientific prowess with societal imperatives. The rigors of scientific inquiry and technological innovation continue to push forward the boundaries of what is possible, driving towards a future where the food on one's plate is as traceable as it is nourishing and safe. The future of food is an intricate mosaic of innovation, responsibility, and potential. As we have explored the tendrils of technology that are entwining themselves into the very DNA of food production and consumption, it is clear that the repercussions will resonate through every level of society. From the fields of farmers utilizing precision agriculture to the kitchens of consumers enjoying extended-shelf-life produce and tailor-made nutrition plans, the landscape of food is undeniably changing. The path forward demands a synthesis of advancement and ethics, ensuring that as we march towards a world that is more efficiently fed, we are also one that honors ecological balance and personal well-being. Our exploration of these themes does not simply close a dialogue but instead opens an ongoing conversation about the sustenance of tomorrow—a conversation that requires the collective engagement and wisdom of farmers, scientists, policymakers, and consumers alike. People also ask : Amidst the exponential growth of technology globally, the food industry is getting a radical makeover, ushering in a new era of automation, precision, and personalization. Topics such as artificial intelligence in food processing, automation and robotics in food preparation, precision agriculture, blockchain in food traceability, and 3D printing for personalized nutrition will be investigated in this piece. These advancements, though disruptive, present us with exciting possibilities to reimagine our food systems today and for the future - making them more efficient, safe, sustainable, and personalised. Artificial Intelligence (AI), once a thing of Sci-Fi movies, is now firmly ingrained in our everyday lives. From digital assistants at home to complex data analysis in corporations, AI has become a ubiquitous component of modern technology. Now, AI continues to make significant strides in a field that is quite dear to us all - our food. Today, let's delve into how AI and machine learning technologies are revolutionizing food processing in the year 2024. Food processing, the core of the food industry, involves a whole chain of activities from procuring raw materials to delivering the final product. It is a complex and multi-stage process with a constant need for precision, hygiene, and efficiency. Enter AI - the game-changer. One of the primary applications of AI in food processing is in quality control. Thanks to modern AI algorithms, computer vision technologies are now able to analyze food items for quality at a speed, accuracy, and consistency that humans could never achieve. These systems, equipped with high-resolution cameras and deep learning capabilities, can identify defects and contaminants, ensuring the safety and quality of food products. But AI’s role in food processing doesn’t end at quality control. Another groundbreaking application of AI is predictive maintenance. AI algorithms can predict equipment failures before they occur, by analyzing patterns and anomalies in operational data. This not only enhances food production efficiency but also significantly reduces costly downtimes, a win for both food companies and consumers. And then we see the advent of smart packaging. Using AI, manufacturers are now creating food packaging that can monitor food freshness, provide nutritional information, and even interact with smart appliances. Imagine a carton of milk in your fridge that signals your smartphone when it's about to go bad. Food waste reduction is yet another significant initiative where AI is leaving its mark. AI models can project demand for food items accurately and optimize supply chains accordingly, effectively reducing surplus production and subsequent waste. As AI continues to evolve, so too does its potential to transform the food processing industry. With further advancements, who knows? Perhaps we might soon see AI robots cooking our meals or even creating new food recipes! As always, the aim of technology is to better our lives by creating easier, faster, and more efficient solutions, and in the realm of food processing, AI sure is living up to this ideal in 2024.Food Tech | What is the new technology in the food industry 2024?
What is the meaning of food tech?
Understanding Food Technology

Impacts of Food tech on Food Industries

Innovations in Food Technology

Challenges in Food Tech

Future of Food Technology
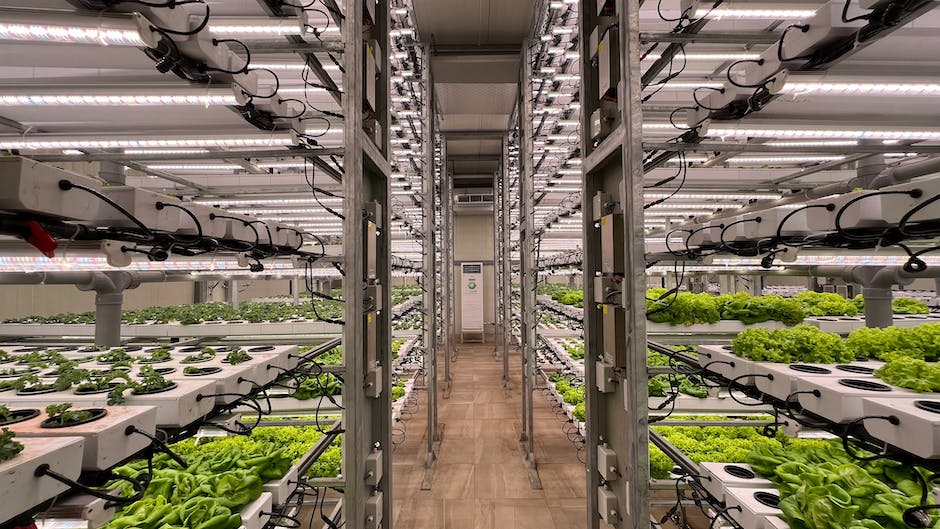

Food Tech
Sustainable Food Production | Food Tech
Catalyzing a Sustainable Revolution: The Role of Food Technology in Agriculture

Alternative Protein Sources | Food Tech
Food Preservation and Shelf-life Extension | Food Tech

Personalized Nutrition | Food Tech

Food Safety and Traceability | Food Tech

What is the new technology in the food industry 2024?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Food Processing
How AI is Revolutionizing Food Processing in 2024
