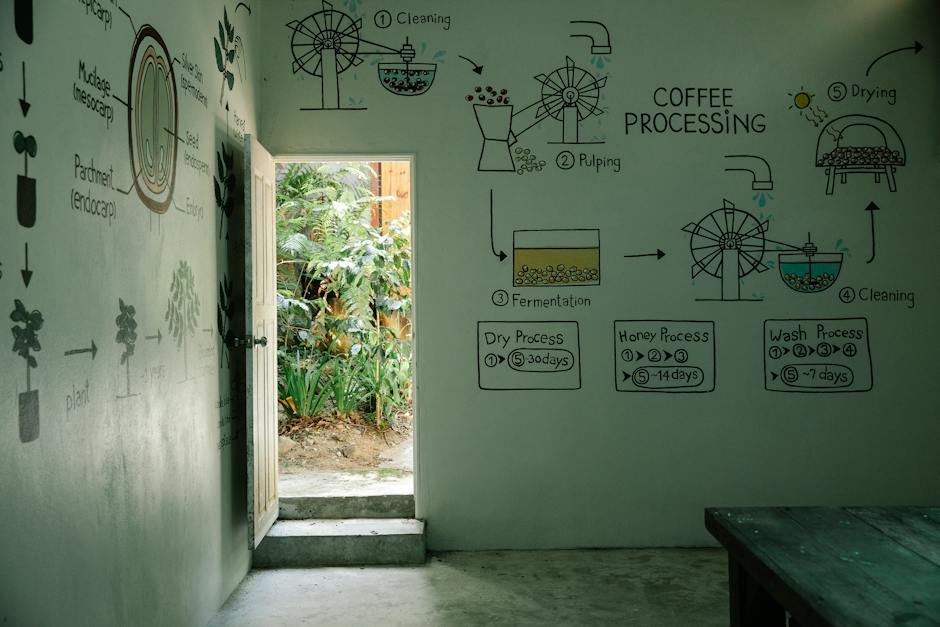
Agridisk
Egypt - Alexandria

Food and Beverage Manufacturing & What is the definition of beverages in the food industry?
Description: The landscape of food and beverage manufacturing is shifting, driven by an intersection of technology, regulation, and evolving consumer preferences. Technological innovations like artificial intelligence, robotics, and digital supply chains are not just modern buzzwords; they are powerful tools that enhance operational efficiency and foster product innovation. Regulatory changes are forcing manufacturers to rethink their strategies, heightening the need for understanding and compliance. Meanwhile, consumer trends such as organic foods, personalized nutrition, and ethical branding shape demand, forcing industry stakeholders to adapt or be left behind. This essay provides a comprehensive understanding of these dynamic elements shaping food and beverage manufacturing today. As technology continues to advance at lightning speed, every industry is experiencing dynamic changes and the food and beverage manufacturing sector is no exception. The digital revolution is reshaping this industry, pushing producers to rethink their traditional methods and embrace innovation in order to stay competitive. One of the most profound ways technology is impacting this sector is through automation. Rapid advancements in robotics and artificial intelligence have given birth to unprecedented levels of productivity and efficiency. Machines can now perform complex tasks from sorting and packaging to quality inspection, all at remarkable speed and accuracy. This not only saves time and resources but also minimizes human error, ultimately driving up profit margins. Additionally, we're seeing a rise in the 'smart factory' concept, leveraging interconnected machines and real-time data to streamline processes. These digitized manufacturing plants hoist efficiency to new heights, greatly reducing costs while increasing productivity. The advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) is at the forefront of this, linking machinery, devices and even people to effectively manage and analyze performance throughout the production cycle. Another significant trend illuminating the food and beverage industry is 3D food printing. This revolutionary method of food production allows for a degree of customization and complexity previously unthinkable. Whether it's creating intricate shapes from pureed foods or developing 'smart' foods with customized nutritional content, 3D food printing has the potential to completely redefine our understanding of food manufacturing. Even on the consumer side, technology is reshaping habits. Applications enabling online ordering, delivery tracking, and personalized nutrition advice are shifting how consumers interact with their food. This digital influence is driving the industry to create products and services that are increasingly personalized, convenient, and able to be delivered directly to consumers' doorsteps. Lastly, blockchain technology is showing significant promise in enhancing transparency and traceability in the food supply chain. This distributed ledger technology can create an immutable record of a product’s journey from field to plate, providing consumers with confidence in the authenticity and safety of their food. In conclusion, the rising wave of technological innovation is revolutionizing the food and beverage manufacturing industry. From smarter factories to emerging trends like 3D printing and blockchain technology, it's an exciting time for this sector. As with any industry evolution, there'll be challenges to overcome. However, those manufacturers who can effectively harness these technologies are poised for exceptional growth and competitive superiority in this rapidly changing business environment. The evolution of regulations in the food and beverage manufacturing industry is fundamentally altering how businesses operate, pushing the boundaries of innovation while ensuring a safer and more sustainable food supply. Simultaneously, emerging factors such as climate change, population growth, and the escalation of consumer demands for transparency and traceability are providing new challenges. One of the key regulatory trends is the burgeoning emphasis on sustainability. To address environmental concerns and ensure long-term resilience, firms are required to reduce water usage, energy consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions. Green packaging also plays a vital role in achieving sustainability goals, necessitating manufacturers to explore combinations of renewable, recyclable, and biodegradable materials. In addition, exhibit an increased focus on food safety regulations that scrutinize elements with a potential impact on public health. This has been manifested in the recent implementation of recalls, withdrawals, and safety notices protocols. Such policy interventions necessitate manufacturers to address quality controls and adhere to standards to prevent contamination and guarantee the healthiness of their products. Further, the evolving regulatory landscape is demanding more transparency in labeling. Consumers want greater access to information about what they are consuming and its origins. Requirements like the listing of genetically modified (GM) ingredients, mention of allergens, and provision for nutritional information on labels are becoming the norm, thus imposing the need for manufacturers to meticulously monitor their supplies and production processes. Regulations are also bridging the gap between the physical and digital worlds in the industry. Compliance with cyber and data privacy regulations has become indispensable, considering the industry's extensive reliance on technology and data. Consequently, manufacturers must incorporate robust cyber hygiene practices and protective data privacy frameworks. The advent of lab-grown or cultured meat has prompted the need for novel regulatory frameworks. Cutting-edge techniques used to produce lab-grown meat necessitates a reinvention of food standards as we know them and requires new methods to verify safety, authenticity, and quality. The introduction of these regulations provides an opportunity for businesses to transform challenges into competitive advantages. Manufacturers that acknowledge the changing regulatory scene, adopt sustainable practices, prioritize food safety, embrace transparency, and stratify their cyber defenses are positioned to excel. In conclusion, the evolution of regulations in the food and beverage manufacturing industry is catalyzing a reinvention of conventional business practices. Manufacturers must discern these changes as a call to evolve, optimize, and innovate to stay ahead in the game. As an industry that nourishes the world, it is beholden upon food and beverage manufacturers to instigate change and implement technologies that rise up to meet the regulatory trends of the future. Consumer trends are ever-evolving, leading those in the food and beverage manufacturing industry to consistently adapt their business strategies. Coupled with these changing consumer habits, other factors such as sustainability initiatives, transparency and regulatory trends, and technological advancements have all made a noticeable impact on manufacturing strategies. Firstly, we're seeing a significant shift towards sustainable, health-focused choices across consumer sectors. This trend continues to influence the manufacturing process as businesses prioritize the use of ingredients that are organic, natural, and locally sourced - aligning to the clean eating and wellness interests of the discerning consumers of today. Businesses are increasingly valuing their alignment with environmental and health awareness while manufacturing their offerings. Secondly, the demand for transparency has compelled businesses to be more accountable for their products. Consumers value honesty and are more likely to stay loyal to brands that practice full transparency, from detailed ingredient lists to disclosing the environmental impact of their production processes. This trend has resulted in the food and beverage industry deploying systems to ensure absolute traceability. Thirdly, novel regulatory frameworks, particularly for emerging food technologies like lab-grown or cultured meat, also shape manufacturing strategies. While these foods could potentially redefine our diets, manufacturers need to successfully navigate regulatory hurdles and public perception. The growing consumer interest in plant-based diets and alternative proteins has also instigated a significant impact. This has not only opened up new, lucrative markets for enterprising businesses but also required manufacturers to retool and rethink the production process to accommodate these novel products. Unquestionably, the increasing focus on cyber and data privacy has a significant influence. As businesses rely more heavily on technology and data, observing data privacy regulations becomes crucial. Finally, the challenges arising from meeting these changing consumer trends represent profound opportunities. Businesses that can transform these obstacles into competitive advantages will stand out in the market. Adapting to changing consumer trends means continually evolving, optimizing, and innovating - not just in product offering, but also in manufacturing strategies. The manufacturing landscape is undoubtedly experiencing a compelling shift, driven by these sweeping changes in consumer trends, which creates an exciting opportunity. The way forward for businesses in the food and beverage industry is clear: adapt, innovate, and keep the needs and wants of the consumers, technology trends, and regulatory environment at the core of their strategy. The complexities of food and beverage manufacturing are demanding, yet they present fertile ground for growth and innovation. Embracing technology, understanding regulations, and responding to consumers' evolving demands are no longer optional; they are imperatives for survival and success in this sector. As we have explored, emerging technologies are transforming operations, regulatory landscapes influence market competition, and consumer trends drive industry innovation. As a result, this evolving landscape requires attention, adaptability, and informed decision-making. These insights serve as a compass for navigating the future of food and beverage manufacturing and the opportunities it holds for industry stakeholders. Navigating the diverse landscape of the food industry reveals a vast array of consumable liquids that we collectively refer to as beverages. These selections are as varied as they are ubiquitous, shaping not only our dietary preferences but also cultural and social customs. The definition of beverages within the food industry is broad, encapsulating a myriad of drinks that range from the morning's first cup of coffee to a celebratory glass of champagne. Within this exploration, we will embark on a journey to classify beverages based on their ingredients, purposes, and effects on the human body, revealing the intricate tapestry that is the beverage sector. Critical insights into the processes that transform a concoction of ingredients into the beverages lining supermarket shelves globally will also be explored, shedding light on the stringent standards and safety protocols that ensure these products are both enjoyable and safe to consume. Beverages hold a significant place within the food industry, encompassing a diverse range of liquid consumables designed for hydration, nutrition, pleasure, or a combination thereof. Their categorization is essential for regulatory standards, consumer transparency, and industry consolidation. Primarily, beverages are classified into two overarching groups: non-alcoholic and alcoholic drinks. Each of these groups is then further subdivided. Non-alcoholic beverages encompass a broad spectrum that includes water—the most fundamental of human needs—followed by soft drinks, such as sodas and carbonated waters, fruit and vegetable juices, and specialty beverages like energy drinks or ready-to-drink teas and coffees. These are further dissected based on their nutritional content and purpose. For instance, sports drinks are engineered to replenish electrolytes and are distinct from nutrient-fortified beverages, which may contain added vitamins and minerals. On the other side of the spectrum, non-caffeinated herbal teas present options marketed for relaxation or medicinal benefits. Alcoholic beverages, on the other hand, are categorized mainly by their production process and alcohol content. They fall into groups such as beers, which are typically brewed from malted barley and hops, wines, which are fermented from grapes or other fruits, and spirits, the result of distilling fermented grain, fruit or vegetables. These distinct processes give rise to a plethora of unique subcategories, such as lagers or ales within beer, or red, white, and sparkling varieties within wine. Alcoholic beverages are subject to rigorous regulation given their psychoactive effects and age-restricted sales, underlining the necessity for stringent categorization within the food industry. The rigorous imposition of standards upon the beverage production process ensures the safety and quality of the consumable offerings that reach the hands of consumers. The adherence to benchmarks such as those laid out by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, as well as international standards provided by the Codex Alimentarius, is paramount. For instance, the meticulous monitoring of the chemical, microbiological, and physical parameters of beverages is a non-negotiable aspect of the production protocol. This includes, but is not limited to, regular testing for contaminants like heavy metals, microbial pathogens, and ensuring correct ingredient labeling to safeguard those with allergies. Furthermore, production facilities are obligated to follow Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs), which encompass a wide array of procedures aimed at guaranteeing a consistently high-quality product. This includes the management of clean and sanitary processing environments, the utilization of quality water sources, and the thorough vetting of suppliers to ensure ingredients meet predefined quality standards. In addition, the implementation of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) systems is a proactive approach to identify potential hazards, thereby allowing for immediate corrective measures to avert adulteration and ensure the integrity and wholesomeness of the beverages. Finally, the traceability and recall mechanisms established within the beverage sector constitute a crucial aspect of consumer protection. In the event that a product is discovered to be in violation of safety standards, prompt and efficient recall procedures are instrumental in mitigating health risks. Equally important are clear labeling practices, which not only inform consumers about the nutritional content and ingredient profile of beverages but also provide critical advisories regarding the presence of potential allergens or substances that may affect certain populations, such as pregnant women or individuals with pre-existing health conditions. The realm of beverages is as complex as it is fascinating, offering a kaleidoscope of flavors, functions, and cultural significances. Through understanding the classifications and production standards, we empower ourselves with the knowledge required to make informed choices about what we drink. As we continue to savor the rich variety of beverages available to us, let's remain appreciative of the meticulous efforts behind each sip—from the careful selection of ingredients to the adherence to rigorous safety standards that uphold the integrity of the global beverage industry. It is this intricate dance between tradition, innovation, and regulation that continues to quench our thirst for both the literal and metaphorical essence of what beverages represent in our lives.Food and Beverage Manufacturing & What is the definition of beverages in the food industry?
Food and Beverage Manufacturing
Technological Impact on the Sector | Food and Beverage Manufacturing

Regulatory and Compliance Developments | Food and Beverage Manufacturing

Consumer Trends and Market Adaptability | Food and Beverage Manufacturing
What is the definition of beverages in the food industry?
Classification of Beverages

Beverage Production and Safety Standards