Agridisk
Egypt - Alexandria

All about modern beverage manufacturing equipment & What are the technological trends in the beverage industry?
Description: Enshrining centuries of ingenuity, modern beverage manufacturing technology represents a microcosm of mankind's relentless pursuit of efficiency and innovation. Charting a course from the rudimentary procedures of yore to today's AI-infused manufacturing landscape, the story of beverage manufacturing illuminates our collective journey towards an optimized future. The convergence of technology, sustainability, and regulatory parameters shapes this industry in fascinating ways, presenting a multi-faceted narrative that explores the glue that holds these pieces together. As we peel back the layers of this complex tableau, we find ourselves entangled in a tale of progress, with each chapter revealing intriguing insights into the components, automation wonder, and the cutting-edge prospects that define beverage manufacturing. From an observational standpoint, tracing the evolution of modern beverage manufacturing equipment manifests as a compelling study heavily influenced by technology as well as human invention and innovation. This article will magnify these transformations, identifying key evolutionary leaps within a timeline characterized by pulsing expansion, discovery, and adaptation. First and foremost, the earliest notable inception moment for beverage manufacturing was ushered in during the Industrial Revolution. The late 1700s saw primitive machinery manifest in the form of steam engines, which were later adapted to drive rudimentary beverage production processes. These developments rendered the traditional manual methods dormant, replacing them with more efficient automated procedures. The late 19th century introduced a significant evolutionary leap – the application of pasteurization to beverage manufacturing. Louis Pasteur’s revolutionary work in 1864 enabled juice, wine, and milk manufacturers to extend their products' shelf-life, boost safety standards and elevate the level of production. Pasteurization functioned as a cornerstone for advancement in beverage manufacturing, laying the groundwork for modern techniques. At the threshold of the 20th century, beverage manufacturing underwent another monumental transformation. The mechanization of washing and filling equipment accelerated production, fueled by the advent of electricity. Additionally, the development of conveyor systems streamlined the bottling process, maximizing efficiency and productivity. The post-World War II era brought about significant advancements in the soft drink industry. In 1957, the invention of the pull-ring tab significantly changed beverage packaging methods. This innovation eliminated the need for additional devices to open the beverage, making the packaging process more cost-effective and efficient. Plastic, a dominant force of the 20th century, played a key role in the evolution of the beverage manufacturing industry. The introduction of PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) bottles in 1973 shaped the course of the beverage industry to the present date. The sanitation, convenience, and cost-effectiveness underscore the immense popularity of plastics in beverage packaging. Advancements in technology have had a profound impact on shaping the modern beverage industry. The inception of digital systems such as PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) have revolutionized process control, monitoring and data management. Given the complexity and volume of manufacturing, these digital systems have rendered the production process more refined and streamlined. Lastly, the 21st century has seen an increasing emphasis on sustainable and green manufacturing practices. Powered by growing awareness about global environmental threats, there's been a profound shift towards energy-efficient manufacturing equipment, waste reduction, and the incorporation of recyclable materials in packaging. Undoubtedly, the journey of beverage manufacturing equipment reflects a deep interplay of technology and human innovation. Each evolutionary leap is founded on and inspired by its predecessors, affirming a continuity that is nothing short of fascinating. With the relentless pace of innovation and ingenuity, it is intriguing to ponder the transformations that the future may hold for beverage manufacturing. Modern beverage manufacturing equipment denotes a vast array of intricate, specialized apparatus intrinsic to the production, packaging, quality control, and distribution of diverse beverages. This orchestration of devices—often a symphony of mechanical, electrical, and automation systems—proffers efficient, high-volume output with rigorous quality measures and increasingly eco-friendly practices. At the heart of each beverage facility exists an intricate pastiche of state-of-the-art machines, each imparting a unique function pivotal in the creation of the end product. Central to these machines are processors or blenders, engineered to concoct beverages with consistency and accuracy. These choreographed devices form the foundation of product creation, ensuring each batch is synonymous with the last. Advanced mixers – such as powder dissolvers and liquid blend systems – enable the stable combination of components, thus leading to homogenous end-products with uniform flavor. Beyond formulation, beverage manufacturers rely on sophisticated filtration systems. This arrangement of complex components covertly filters fragments and sediments, safeguarding the integrity of the final product. Predominantly mechanized, these systems often employ membranes or pads to filter unwelcome particles, ensuring consistency in both taste and texture. Equally paramount, carbonation is a process often utilized, primarily in the production of fizzy drinks. Supplementing bubbles under standard conditions necessitates specialized carbonation machinery. The methodology typically includes dissolving carbon dioxide under pressure in a pre-chilled liquid, thereafter maintaining the pressure until the beverage is sealed, proffering that delightful effervescence on liberation. Packaging follows product creation and refinement, signaling a vital phase demanding advanced mechanical equipment. Bottling and canning machines, equipped with hygienic high-speed filling and sealing capabilities, are integral to this stage. Technological strides in robotics have augmented this process, with robotic arms now seamlessly orchestrating filling operations, thereby magnifying precision and speed while mitigating human error. Thereafter, the drinks are capped or sealed with innovative devices—From twist caps to pull-tabs—each method contributing its distinct appeal alongside practical benefits. This is followed by label applicators that brandish each product with its defining visual identity, firmly establishing it in the minds of consumers. Inspection systems hold an often-underappreciated role, albeit a critical one, in ensuring the delivery of faultless products. Advanced instruments—such as X-rays, cameras, and fill-level detectors—are deployed to discern any inconsistencies. Rigorous checks for fill levels, sealing, and label integrity ensure consumer satisfaction and safeguard the brand reputation. With heightened focus pulsating on sustainability, machine manufacturers are progressively integrating energy-efficient and water-conserving features. Variable frequency drives (VFDs), for instance, reduce energy usage by matching motor speed to actual load, while water recovery systems curtail water wastage during sanitation by systematically recycling it. To surmise, modern beverage manufacturing ingenuity navigates a terrain of intricate equipment, from processors to inspection systems, each with their distinct, indispensable sport. They all serve in unison to deliver the symphony of flavors we, as consumers, enjoy today, with an added focus on environmental stewardship shaping the narrative in the new epoch. Today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape is embracing intelligent automation and AI, and nowhere is this more prevalent than in the beverage industry. This industrial evolution, akin to the introduction of steam engines and PLCs, effectively modernizes the sector as technology constantly progresses. The deployment of automation and AI brings about a new age of streamlined operations and enhanced performance in beverage production and packaging, further revolutionizing the industry. With the advent of automated systems, tasks that previously required human intervention have been relegated to robotic arms and sensors, increasing efficiency and accuracy. Alongside this, the incorporation of AI allows for real-time optimization of these tasks, with procedural adjustments made as conditions necessitate. Central to this development is the role of collaborative robots or 'cobots', designed to operate symbiotically with human counterparts. These cobots can conduct repetitive tasks such as picking, placing, and sorting beverage containers, reducing errors and potentially increasing production output. Moreover, AI interfaces with instruments like Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) devices provide for predictive maintenance, identifying potential faults before they become disruptive. This foreknowledge enhances operational continuity, minimizes production downtime and could potentially save manufacturers significant financial costs annually. Similar AI applications extend to quality control, where advanced vision systems and hyperspectral imaging techniques identify irregularities in both filled and empty bottles and cans, ensuring product quality and maintaining brand reputation. Of significant impact is AI's role in enhancing sustainability in beverage manufacturing. AI applications such as smart meters enable companies to monitor real-time energy consumption and use this data to optimize efficiency. AI also has the potential to optimize water use, one of the industry's most significant sustainability challenges, through cognizant process control. Furthermore, AI can evaluate supply chain optimization, reducing the carbon footprint associated with transportation and packaging. Just as revolutionary past innovations, like pasteurization and PET bottles, reshaped the industry, the paradigm shift to automation and AI offers limitless possibilities for the beverage industry. Robotic technology in packaging and AI-optimized energy management are just the tip of the iceberg in this current Industrial Revolution. In conclusion, the deployment of automation and AI in modern beverage manufacturing is not merely a convenience but a necessity to keep pace in a fiercely competitive and dynamic industry. It signifies a new era of beverage production, one that's characterized by efficiency, accuracy, quality, and a commitment to sustainability. The harmonious intersection of machinery and AI algorithms defines this contemporary view, echoing the intrigue of an industry constantly on the precipice of the next great revolution. Regulatory standards play a critical role in guiding the use of modern beverage manufacturing equipment. They ensure product safety, quality, and consistency. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees these regulations under the Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act and amendments such as the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA). These provide specific guidelines regarding cleanliness, machine maintenance, and operation. FSMA, enacted in 2011, places a greater emphasis on preventing food safety issues including the contamination of beverages. Globalization, in the context of the beverage industry, has seen the emergence of standards that transcend national boundaries. The International Organisation for Standardization (ISO), specifically ISO 22000, sets comprehensive food safety management standards that encompass the entire food chain from farm to fork, or in this case, from water source to the consumer's glass. Beyond safety and quality, the landscape of regulatory standards has also begun to address sustainability—taking into account environmental, economic, and social factors. ISO 14001, the Environmental Management Systems standard, provides guidance for organizations seeking to manage their environmental responsibilities effectively. Where sustainability is concerned, Beverage Industry Environmental Roundtable (BIER) has taken contemporary leadership. BIER is a technical coalition of leading global beverage companies working together to advance environmental sustainability within the beverage sector. Through collaborative action and transparency, BIER actively addresses industry-wide challenges related to water stewardship, energy conservation and climate change, advocate for effective and efficient policy and regulations, and increase public awareness of the significance of sustainability in the beverage sector. Within the manufacturing processes themselves, sustainability is being championed through the sophisticated use of energy-saving technologies—high-efficiency boilers, motors and LED lighting, optimized heating and cooling systems, energy recovery from waste streams—or even deriving energy from renewable sources such as solar and wind power. Within the realm of packaging, the focus has shifted towards bio-degradable and recyclable materials, reduction of package weight, or moving towards a circular economy model where waste is significantly minimized. Innovations in digital technologies including data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence (AI) are providing new avenues for enhancing sustainability. These innovations offer the capability to optimize production efficiency, reducing resource usage and minimizing waste. Furthermore, AI enables predictive maintenance—detecting problems before they occur. This substantially reduces both operational downtimes and the energy-intensive start-up and shut down sequences of the manufacturing equipment. In conclusion, the modern regulatory landscape is multifaceted, encompassing not just the crucial aspects of safety and quality, but also venturing into sustainability. As this evolution continues, leveraging both technological innovations and progressive industry coalitions such as the BIER holds significant potential in steering the beverage industry towards ever-greater levels of sustainability. As the course of this journey unfolds, the impact on our planet and society promises to be genuinely refreshing. As the frontiers of technological advances continue to extend, the future of beverage manufacturing is likely to be shaped by a multitude of emerging trends. At the nexus of technological innovation and beverage manufacturing, the following trends are poised to redefine the industry in unprecedented ways. Implementing Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) is no longer a far-off fantasy, but an impending reality for the beverage manufacturing industry. These complementary technologies could streamline production processes by offering prescriptive insights based on data gleaned from equipment sensors and connected processes. This could substantially optimize energy consumption, water utilization, and waste reduction. Furthermore, AI and IoT have the potential to revolutionize supply chain management by providing real-time tracking and predictive analytics, ultimately improving efficiency and reducing a factory's carbon footprint. There is an accelerating trend towards Intelligent Automation. Complex algorithms, combined with machine learning, can automate decision-making processes, thereby increasing production speeds, improving product quality, and reducing human error. The more these intelligent systems 'learn,' the better they become at making informed decisions, effectively becoming a driving force behind increased productivity and reduced costs. The utilization of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) in beverage manufacturing is another emerging trend. These technologies could render traditional training and troubleshooting methods obsolete, providing a more effective and immersive experience. AR/VR enabled maintenance could lead to fewer equipment downtime instances and enhance operator efficiency, while AR/VR in training could expedite employee onboarding and improve safety standards. Beverage manufacturers are also embracing the transition towards smart factories. In these highly digitized and connected environments, all devices, systems, and processes communicate with each other seamlessly. All data is shared in real-time, promoting optimal efficiency, flexibility, and autonomy, thus enabling manufacturers to respond to changing market demands promptly and efficiently. Meanwhile, the increasing focus on sustainable and biodegradable packaging solutions is another trend not to be overlooked. As consumers become more eco-conscious, the demand for green packaging is invariably growing. To this end, a potential game-changer could be the development of edible packaging derived from seaweed or algae. Its potential for revolutionizing beverage packaging by reducing plastic waste is exciting and could have a significant impact on sustainability goals. Lastly, the revamped focus on personalized nutrition is enabling the development of 'smart' beverages tailored to individuals' unique nutritional needs. Advances in AI, genome sequencing, and microbiome analysis are expected to contribute to this trend, making personalized beverages an integral part of preventative healthcare and lifestyle. Undoubtedly, these emerging trends – driven by potential-filled technologies – are set to redefine the future of the beverage manufacturing industry. As these trends gain traction, the industry must align itself with these changes to remain competitive and fulfill the evolving demands of discerning consumers. The marriage of technology with beverage manufacturing undeniably carries the promise of a more efficient, innovative, and sustainable future. Drawing an arc from the evolution of beverage equipment to the envisioned frontiers of technology, we have embarked on a profound exploration of a compelling narrative. This complex weave of history, innovation, regulatory complexity, and sustainability paints the creation of our favorite beverages in a light that merges art and science in the most compelling ways. The future, replete with IoT-enabled machinery and predictive maintenance, both challenges and excites, as we stand on the precipice of transformations yet unraveled. As we consume our preferred drinks, let's raise a toast to the intricate web of processes and systems that ensure such perfection flows into our cups, unremittingly pushing the boundaries of technology and human capability for a more efficient, sustainable future. The beverage industry is a dynamic sector where innovation thrives, continually reshaping the landscape of production, packaging, and distribution. Technological advancements are perpetually brewing beneath the surface, with progressive trends such as smart packaging and IoT integration leading the charge. These innovations are not just transforming how we interact with our favorite drinks but also redefining the standards of quality and engagement. From ground-breaking uses of artificial intelligence and machine learning that fine-tune operations to the sustainability strides being made through renewable energy and eco-friendly materials, the beverage world is a testament to the power of technology catalyzing positive change. As we delve into the intricacies of these trends, one thing becomes clear: the future of beverages is as exhilarating as it is effervescent. In the constantly evolving field of packaging science, the integration of 'smart' technology into beverage containers heralds a new era of consumer interaction. Smart packaging, characterized by its capacity for communication, responsiveness, and distinct functionality, significantly enhances the consumer experience whilst offering unprecedented utility in tracking and maintaining product integrity. This transformative approach to packaging is not simply a matter of convenience; it serves as a touchstone in the ongoing journey toward comprehensive consumer engagement and product stewardship. The defining feature of smart packaging is its ability to communicate. Beverage containers are now equipped with QR codes and Near Field Communication (NFC) tags, which when scanned by a smartphone, reveal a wealth of product information. Consumers are granted access to data ranging from nutritional content and ingredients to the provenance of the beverage – a degree of transparency that symbolizes fidelity and bolsters brand loyalty. This interaction cultivates an informed consumer base, empowered in their purchasing decisions by a depth of knowledge traditionally unavailable at the point of sale. Beyond communication, smart packaging plays a fundamental role in safeguarding product integrity. Embedded sensors within packaging monitor critical parameters such as temperature and pH levels, guaranteeing that the beverages are consumed at their optimal quality. This ability to track the conditions of the product through the supply chain mitigates the risk of spoilage and extends shelf life—factors of particular importance in the meticulous field of perishable goods. The convergence of packaging and interactive technology has introduced a new dimension of consumer engagement. Beverage companies now employ smart packaging as a portal to immersive experiences; a simple tap of a smartphone can launch interactive games, promotional offers, or loyalty programs. The aim is to create a lasting bond between the brand and the consumer, transforming a routine act of consumption into a unique and memorable interaction. Moreover, the application of intelligent packaging solutions offers a platform for addressing environmental concerns associated with beverage containers. Features such as indicators that inform consumers when a product is reaching the end of its shelf life aid in reducing waste. Furthermore, the development of smart packaging materials that communicate their own recyclability encourages responsible disposal and amplifies the industry's move toward sustainability. In conclusion, the infiltration of smart packaging into the beverage industry augments the bond between consumers and products. It marks a salient advance in consumer intelligence, product safety, engagement, and ecological conscientiousness. This sophisticated integration of technology into something as customary as a beverage container is a testament to the potency of innovation in reshaping industries and redefining the scope of consumer interaction. One of the most significant developments is the use of biodegradable and bio-based materials for packaging. Companies are exploring substitutes for fossil fuel-based plastics with plant-based alternatives, such as PLA (polylactic acid) derived from cornstarch, and other biopolymers that break down more easily in the environment. These materials aim to reduce the carbon footprint and post-consumer waste associated with beverage packaging. Water usage presents another critical facet of sustainable beverage production. The industry has traditionally been water-intensive; however, recent advancements include the implementation of water recovery and reuse systems. These systems are designed to treat and repurpose wastewater resulting from production processes, thereby reducing overall water consumption and lessening the impact on local water resources. Energy consumption, too, is a focal point of sustainable innovation. Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are becoming more commonplace in providing the electricity needed for production facilities. Not only do these sources curtail reliance on fossil fuels, but they also offer the potential for reducing operational costs over time. State-of-the-art facilities are being equipped with energy-efficient machinery to minimize energy usage without compromising efficiency or product quality. Beyond production and materials, sustainable beverage production also emphasizes the agricultural origins of the products. Sourcing ingredients from organic farms and those practicing regenerative agriculture is gaining traction. Such agricultural techniques aim to restore soil health, sequester carbon, and support biodiversity, which, in turn, fosters a more resilient and sustainable supply chain for the beverage industry. Similarly, a transparent and ethical supply chain is crucial to sustainability. Beverage companies are increasingly expected to verify that their ingredients are sourced responsibly and that the farmers and workers involved in the process are treated fairly. This ethical dimension not only ensures the sustainability of the human element within the industry, but it also strengthens the bonds between consumer and product, as ethical considerations are factually intertwined with purchasing decisions. In conclusion, it's apparent that the future of beverage production is inherently linked with sustainable practices. The industry's commitment to adapt and innovate is setting a template for how to operate responsibly while still serving the needs and desires of the global consumer base. The integration of eco-friendly materials, conservative water and energy use, support for sustainable agriculture, and ethical supply chains demonstrates a significant shift towards a future where beverage production strives not only for profitability but also for environmental stewardship and social responsibility. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are markedly transforming beverage manufacturing, apart from the previously discussed advancements. Beyond packaging and sustainability, these technologies are dramatically reshaping production processes, quality control, and market research, thus heralding a new era in consumer insights. One significant development is the integration of AI in beverage formulation. Machine learning algorithms are now able to analyze vast amounts of data regarding flavor combinations and consumer preferences. As a result, manufacturers can create new beverage formulas that cater to the evolving tastes of the market. These AI-driven systems can predict which flavors might appeal to certain demographics or suggest unique ingredient combinations that have not yet been explored. Quality control has been revolutionized with the aid of AI, which can now predict and identify potential defects and contaminants faster and more accurately than ever before. Drones and smart cameras equipped with imaging technology scan products and equipment for any irregularities, ensuring consistent quality and compliance with safety standards. Machine learning algorithms are also adept at anticipating equipment failure or maintenance needs, reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency. In the realm of consumer insights, AI is providing a more nuanced understanding of purchasing behaviors. Machine learning models can analyze data from points of sale, social media, and other digital footprints to identify emerging trends and preferences. These insights are invaluable for beverage manufacturers looking to fine-tune their marketing strategies and product offerings. AI's capability to sift through large datasets enables a precision-targeted approach to product development, ensuring that new beverages meet the specific desires of targeted consumer segments. Moreover, AI is instrumental in supply chain optimization. By forecasting demand more accurately, manufacturers can reduce overproduction and waste. Intelligent systems are capable of managing inventory with high efficiency, ensuring that the flow of materials and products is well-coordinated with actual market needs. This optimization ultimately contributes to a more sustainable manufacturing process by minimizing excess and inefficiency. In addition, machine learning is pivotal in predicting the outcomes of climate and its impact on crop yields. This predictive capacity allows manufacturers to prepare for potential ingredient shortages by adapting sourcing strategies in advance, thereby sustaining a steady supply chain and stabilizing pricing in volatile markets. Finally, in the production line, AI-enabled robotics have become indispensable. These robots can perform tasks with precision and speed, from bottling to packaging, minimizing human error and increasing productivity. The collaborative efforts of human workers and robotic systems ensure that beverage production meets high standards of quality and efficiency, while also opening avenues for innovative manufacturing methods. The application of AI and machine learning within the beverage industry underscores a fundamental shift towards data-driven decision-making. These technologies enable a deeper comprehension of both the product lifecycle and consumer behavior. By leveraging the power of AI and machine learning, the beverage sector is not only enhancing its capabilities in creating superior products and experiences but is also leading the way in sustainable and responsible manufacturing practices that are mindful of societal and environmental impacts. Abstract: When one pours a beverage, there is an oft-unseen bulwark standing between the purity of that drink and a myriad of potential contaminants. This unsung hero is none other than the advanced filtration and processing techniques rigorously employed in contemporary beverage production. It is these methodologies that guarantee the delivery of consumables held to the highest standards of quality and safety. Filtration Fundamentals: More Than a Sieve Beyond mere sieves, modern filtration employs preciseness on a microscopic level. The crux of this technology lies in membrane filtration — a resolute process capable of removing foreign particles as small as bacteria, and in some instances, even viruses. These sophisticated membranes act as selective barriers, permitting only water and desired solutes to pass through their meticulous pore structure. Microfiltration and Ultrafiltration: The Vanguard of Purity Microfiltration and ultrafiltration are paramount in the hierarchy of beverage purification. Microfiltration, with pores ranging from 0.1 to 10 micrometers, excels in extracting larger pathogens and suspended solids. Descending further into minute detail, ultrafiltration with pores from 0.001 to 0.1 micrometers adeptly sequesters colloids, proteins, and even minute pathogens, ensuring that both clarity and microbiological integrity are upheld. Reverse Osmosis: A Molecular Level of Cleanliness An additional fortification in beverage safety is reverse osmosis (RO). This process, driven by high pressure, propels water through a semipermeable membrane, rigorously excluding dissolved salts, sugars, and other impurities. RO is indispensable in producing not just safe, but also palate-pleasing beverage products by enabling the control and standardization of water composition, a critical ingredient in all beverages. Processing Prowess: Past Pasteurization Thermal processing, historically typified by pasteurization, has evolved. High-pressure processing (HPP), for example, neutralizes pathogens without thermal intervention, thereby preserving the nutritional and sensory attributes of beverages - a delightful boon for the discerning consumer. HPP harnesses intense pressure to disrupt cellular activity of possible contaminants, extending shelf life while maintaining a product's "fresh" status. Aseptic Processing: The Armor Against Post-Processing Contamination Aseptic processing stands as a testament to the continual efforts to elevate beverage safety. After sterilization, the product and the package are brought together in a sterile environment, thwarting contact with any contaminants. This coupling not only extends shelf life but also widens the geographical reach of distribution without resorting to refrigeration, magnifying the accessibility of quality beverages on a global scale. In Summation: While the beverage industry dynamically evolves, advanced filtration and processing techniques remain rooted in the foundational quest for uncompromising quality and safety. These methods are the silent yet steadfast guardians of our beverages, ensuring that each sip taken is not just a refreshing indulgence but also a testament to the rigorous science that shields our well-being. Transparency and efficiency are cornerstones of a highly functional beverage supply chain. The implementation of blockchain technology has the capability to revolutionize this intricate system. By its decentralized nature, blockchain harbors the potential to instill a level of trust and verification that traditional methods struggle to achieve. Blockchain operates on a system of distributed ledgers that record transactions across many computers, ensuring that each entry is both irreversible and transparent. In the context of the beverage industry, blockchain can be harnessed to provide a comprehensive and immutable record of every transaction—from sourcing of raw materials to the delivery of products to consumers. One paramount aspect of utilizing blockchain within a beverage supply chain is the traceability it affords. Every step of a product’s journey can be documented and easily accessed, which allows for swift identification of sources in the event of contamination or recall. Thus, not only is consumer safety enhanced, but it also empowers manufacturers to rectify issues expediently. In terms of efficiency, blockchain mechanizes the administrative processes that are typically prone to human error or fraud. Smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code—can automate payments and transfer of ownership, ensuring that suppliers and distributors are compensated on time and accurately. This reduces administrative burdens and the likelihood of disputes, leading to smoother operations. However, the successful implementation of blockchain is contingent upon robust participation and data integrity. All entities involved in the supply chain—from farmers to distributors—must commit to consistently recording data onto the blockchain. The increased visibility and scrutiny could disincentivize malpractices, such as the adulteration of products or misleading claims about provenance. The environmental sustainability of blockchain itself requires examination. The energy consumption of blockchain networks is a topic of extensive debate; therefore, it is essential for the beverage industry to adopt blockchain configurations that are energy efficient to maintain alignment with sustainability goals. Moreover, the emphasis on consumer engagement cannot be understated. Blockchain can serve as a portal through which customers learn about the lifecycle of their beverage, fostering a connection with the product that is rooted in trust and appreciation for the ethical and sustainable sourcing of ingredients. The intersection of blockchain with existing advancements signals an exciting fulcrum point for the beverage industry. When paired with AI, biodegradable packaging, and sustainable practices, blockchain forms an integral part of an innovative, environmentally conscious approach that can redefine the relationship between producers, consumers, and the planet. In conclusion, the deployment of blockchain technology in the beverage supply chain can indeed elevate both transparency and efficiency. As the sector continues to evolve, we can anticipate that the embracement of such technological advancements will become the linchpin for consumer trust, regulatory compliance, and environmental stewardship within the industry. As we pour over the recent advancements defining today's beverage industry, it is evident that technology continues to serve as the cornerstone for innovation. The fusion of AI, IoT, blockchain, and sustainability practices is creating a concoction of efficiency, personalization, and environmental responsibility that is both refreshing and necessary. While taste and tradition will always remain central to the industry, these technological trends are the key ingredients in the recipe for future success. They not only quench the consumer's thirst for quality and transparency but also demonstrate the industry's commitment to crafting a future that is as sustainable as it is satisfying. Cheers to an exciting journey ahead, one overflowing with opportunities and innovation at every turn.All about modern beverage manufacturing equipment
Evolution of Beverage Manufacturing Equipment

Components and Functions of Modern Beverage Equipment

Automation and Artificial Intelligence in Beverage Manufacturing
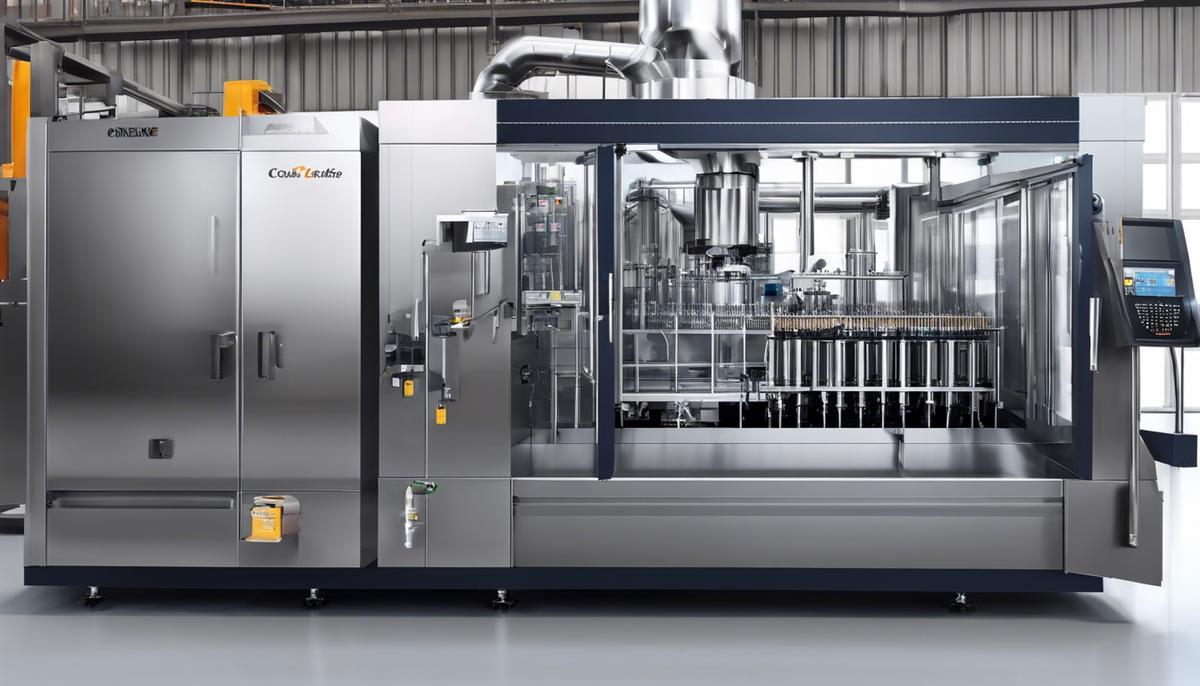

Regulatory Standards and Sustainability in Beverage Manufacturing
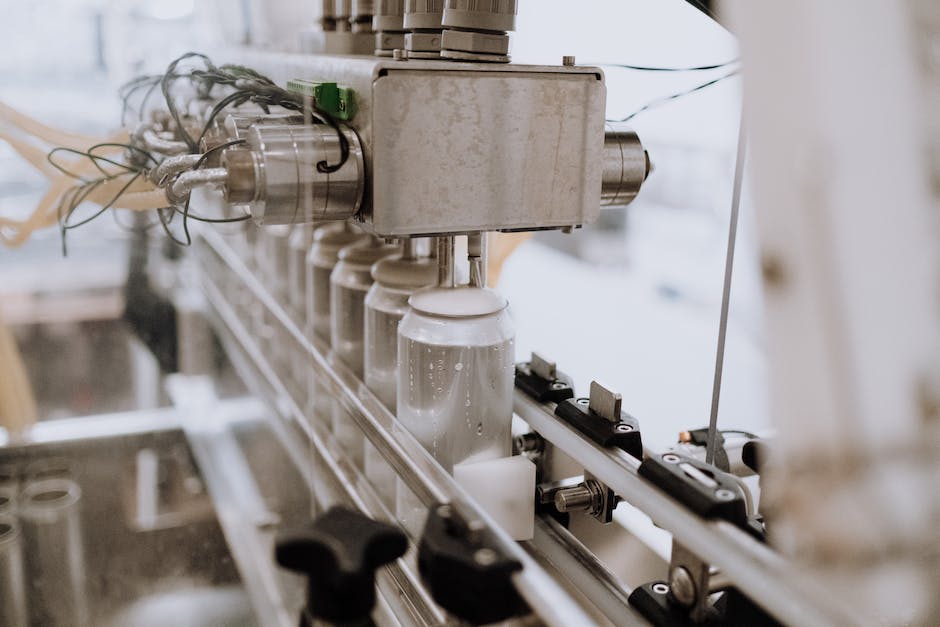

Future Prospects in Beverage Manufacturing Technology
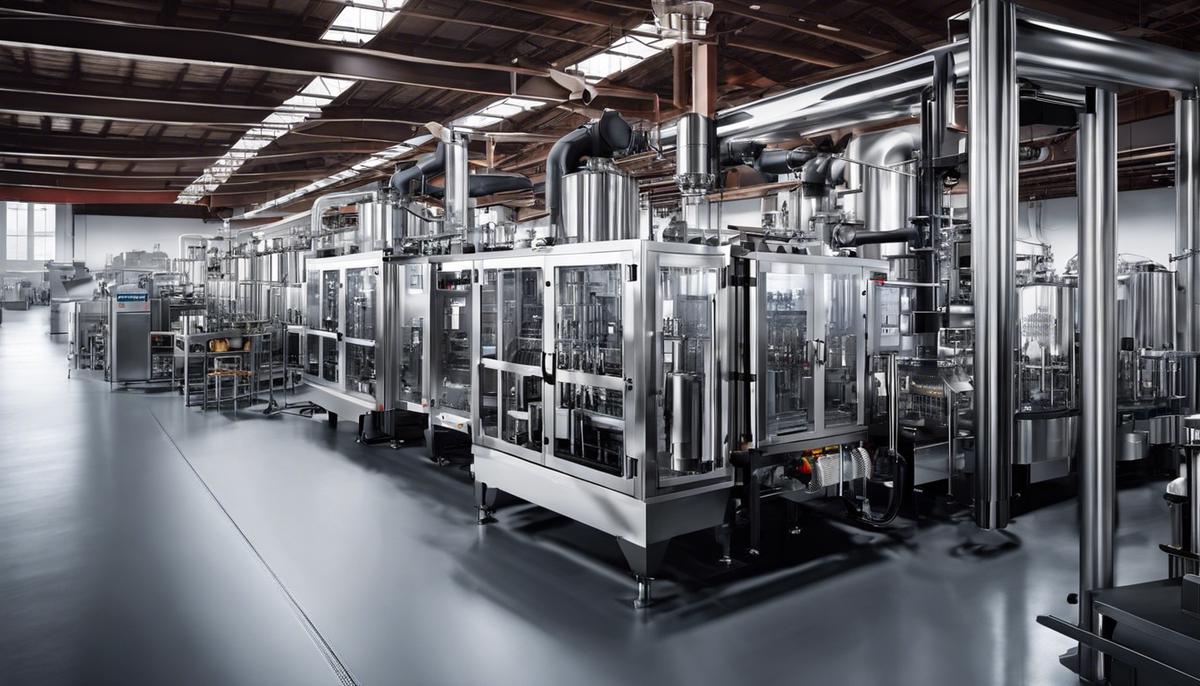

What are the technological trends in the beverage industry?
Smart Packaging and IoT Integration
The Emergence of Intelligent Packaging in the Beverage Sector
Communication At the Forefront
Ensuring Product Integrity
Interactivity and Consumer Engagement
Driving Sustainability

Sustainability and Renewable Energy
Advances in sustainability within the realm of beverage production are rapidly evolving, guided by both innovation and necessity. The industry is currently witnessing a formative shift away from traditional practices, primarily to address environmental concerns and to meet consumer demands for ecologically responsible products. As our collective awareness of sustainability issues intensifies, the beverage sector is adapting with novel methods and materials that promise to redefine production from the ground up.
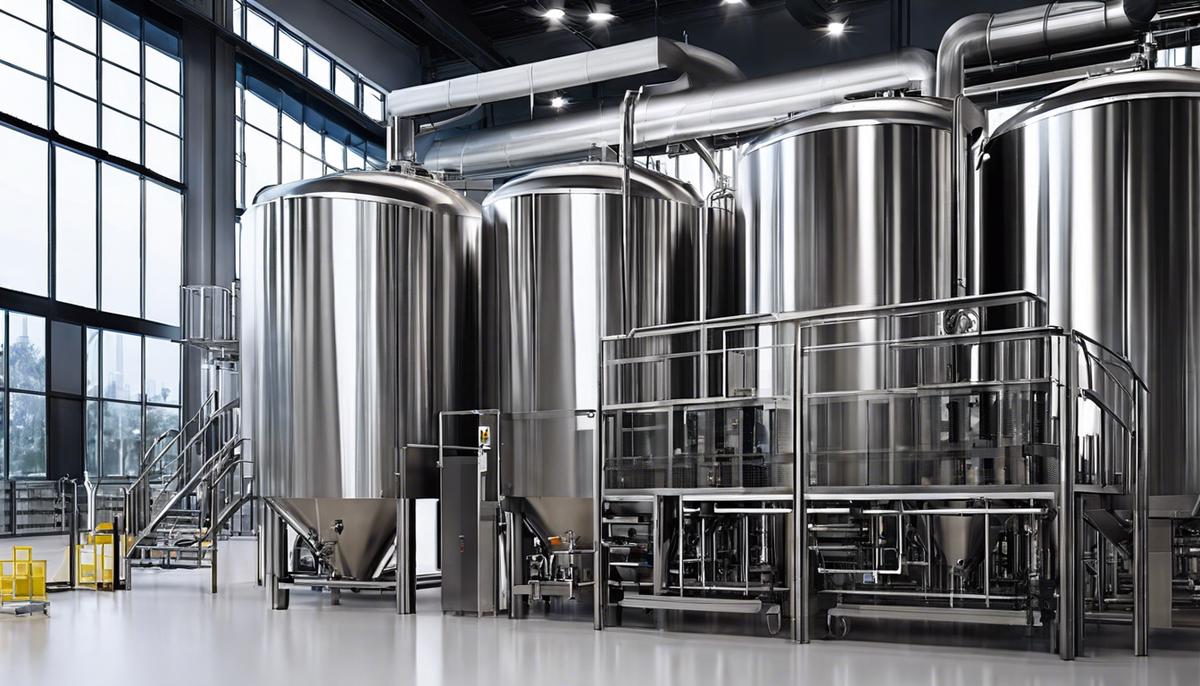

Artificial Intelligence and Fodd Machine Learning

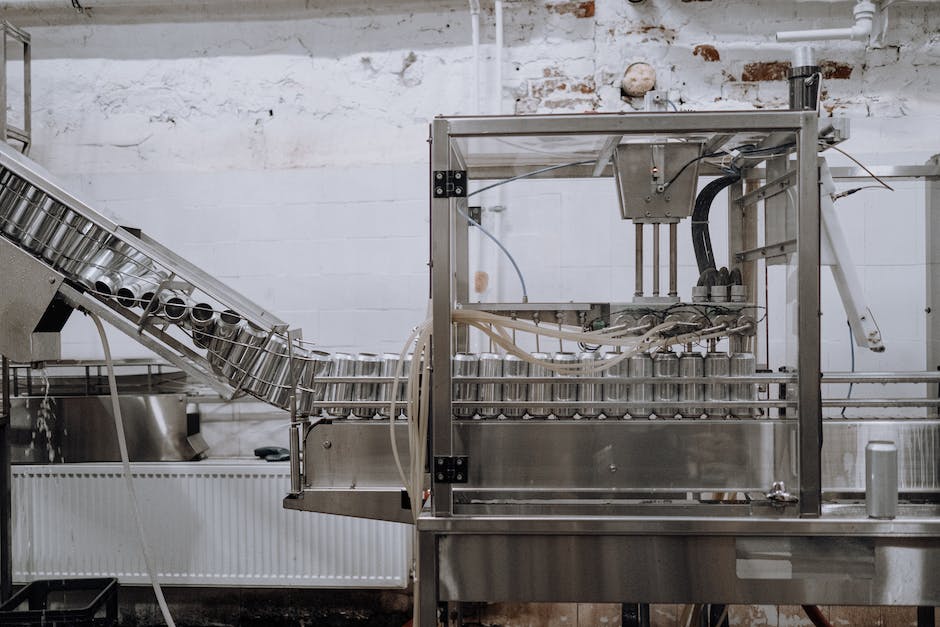
Advanced Filtration and Processing Techniques
The Minutiae of Micron-Level Filtration: Secure Guardian in Beverage Quality Assurance

Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency